 |
| From https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Holder_table_function.pdf |
def holder_table(x0,x1): return -abs(sin(x0)*cos(x1)*exp(abs(1-sqrt(x0*x0+x1*x1)/pi))) x,y = dlib.find_min_global(holder_table, [-10,-10], # Lower bound constraints on x0 and x1 respectively [10,10], # Upper bound constraints on x0 and x1 respectively 80) # The number of times find_min_global() will call holder_table()
Or in C++:
auto holder_table = [](double x0, double x1) {return -abs(sin(x0)*cos(x1)*exp(abs(1-sqrt(x0*x0+x1*x1)/pi)));}; // obtain result.x and result.y auto result = find_min_global(holder_table, {-10,-10}, // lower bounds {10,10}, // upper bounds max_function_calls(80));
Both of these methods find holder_table's global optima to about 12 digits of precision in about 0.1 seconds. The documentation has much more to say about this new tooling. I'll also make a blog post soon that goes into much more detail on how the method works.
Finally, here are some fun example outputs from the new semantic segmentation example program:
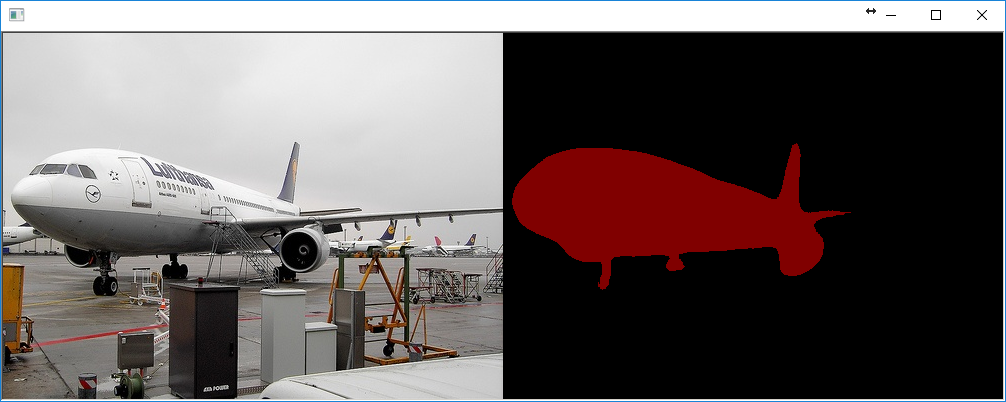
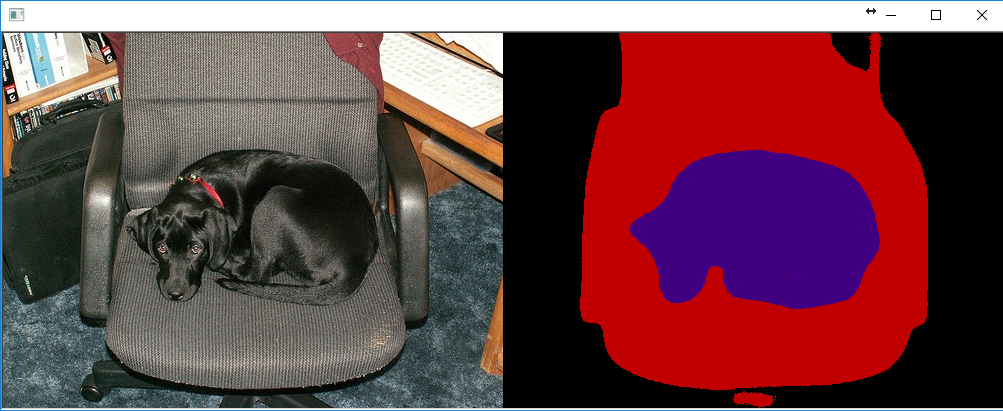




Awesomme!! Looking forward to more explanations on global optimizer.
ReplyDeleteAwesomme!! Looking forward to more explanations on global optimizer.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThanks a lot, Davis, great library!
ReplyDeleteIs it possible to build dlib-GPU-based solution, so that result program could work both on user computers with GPU and on computers without CUDA-supporting GPU, in CPU mode only?
Andrey Zakharoff >> Yes, you can do it. You need check_cuda start file, which load cuda library dynamically and check compatibility with cuda. After it you run one of two files - first compiled with cuda, second compiled for cpu only. For cpu you can use lapack, which dramatically improved your cpu version. Also cpu and gpu version inside are the same. You need only set flags for compiler.
ReplyDeleteI do it for windows and mac (4 result files) and it works perfectly.
What is the speed of the semantic segmentation?
ReplyDeleteHi Davis;
ReplyDeleteAs I understand from the semantic segmentation training code in file http://dlib.net/dnn_semantic_segmentation_train_ex.cpp.html, I can train a new model on another dataset as long as I give the corresponding vector to the trainer. Is that right and if so, do I need to do any change in network types in file http://dlib.net/dnn_semantic_segmentation_ex.h.html ?
thanks in advance
Yes, that's right. Giving it different training data is fine.
ReplyDeleteHi again Davis,
ReplyDeleteI need probability as well as class label for each pixel. I thought changing the to_label function of loss_multiclass_log_per_pixel_ class such that I will also get the value not only the label. Is this a correct way or do you have any other suggestions?
thanks.
Yes, the log loss optimizes the log likelihood and is what you should use. Then you will get something that outputs log likelihoods. Convert them to probabilities by passing them through a sigmoid.
ReplyDeleteIn the segmentation example code, after these codes:
ReplyDeleteanet_type net;
deserialize("semantic_segmentation_voc2012net.dnn") >> net;
I add these lines:
softmax probabilities;
probabilities.subnet() = net.subnet();
but at this point I could't solve how to iterate likelihoods of classes for each pixel.
Can you give me some tips?
The CNN face detector can run on the GPU. But the HOG detector is unchanged and single threaded. If you want to use multiple threads to run the HOG detector then the user should do so, by making multiple threads themselves and processing many images in parallel.
ReplyDelete